TL;DR
- AI-powered role-playing enables scalable, measurable, and individualized training for leaders, especially for emotionally challenging conversations.
- Success depends on strategic preparation, piloting, continuous optimization, and integration into existing HR processes, with acceptance and technical infrastructure being crucial.
- Personalized, data-driven analyses and industry-specific adaptations sustainably improve leadership development and support an open, culturally adapted feedback and learning culture.
HR development faces a fundamental challenge: How do we develop leadership competencies that cannot be taught in seminars but only acquired through practical exercise? Conducting critical feedback conversations, resolving conflicts, motivating employees – these skills don't arise from theory, but from repeated practice in realistic situations.
AI-powered role-playing for the first time offers the opportunity to train difficult leadership conversations in a safe environment – scalable, measurable, and individually adaptable. This guide shows HR teams specifically when its use is beneficial, how implementation succeeds, and which success metrics are relevant.
When are AI role-plays useful for HR development?
Identifying the right use cases
AI role-plays unleash their strength when:
- Scaling is required You have more than 8 leaders who need to be developed simultaneously. Traditional coaching programs quickly reach capacity limits here, while AI systems scale from 10 to 100 leaders – without additional trainer capacities or coordination effort.
- Difficult conversations are avoided Critical feedback conversations are postponed, terminations are communicated too late, conflicts simmer for months. The reason is not a lack of knowledge, but a lack of practice. AI role-plays enable risk-free training of these emotionally challenging situations.
- Uniform leadership quality is lacking Team A experiences empathetic leadership, Team B authoritarian approaches – inconsistent leadership styles harm corporate culture. AI-based training conveys uniform standards and documents whether these are actually applied.
- Traditional methods are not sustainably effective After classic seminars, the effect dissipates in everyday life. The reason: a one-time role-play with colleagues, then never again practical application. AI systems enable continuous training between meetings.
- Measurability is demanded Which leaders need more support? Where do trainings work best? External seminars provide participation certificates – no real insights. AI platforms offer detailed analytics on learning progress, skill gaps, and training effectiveness.
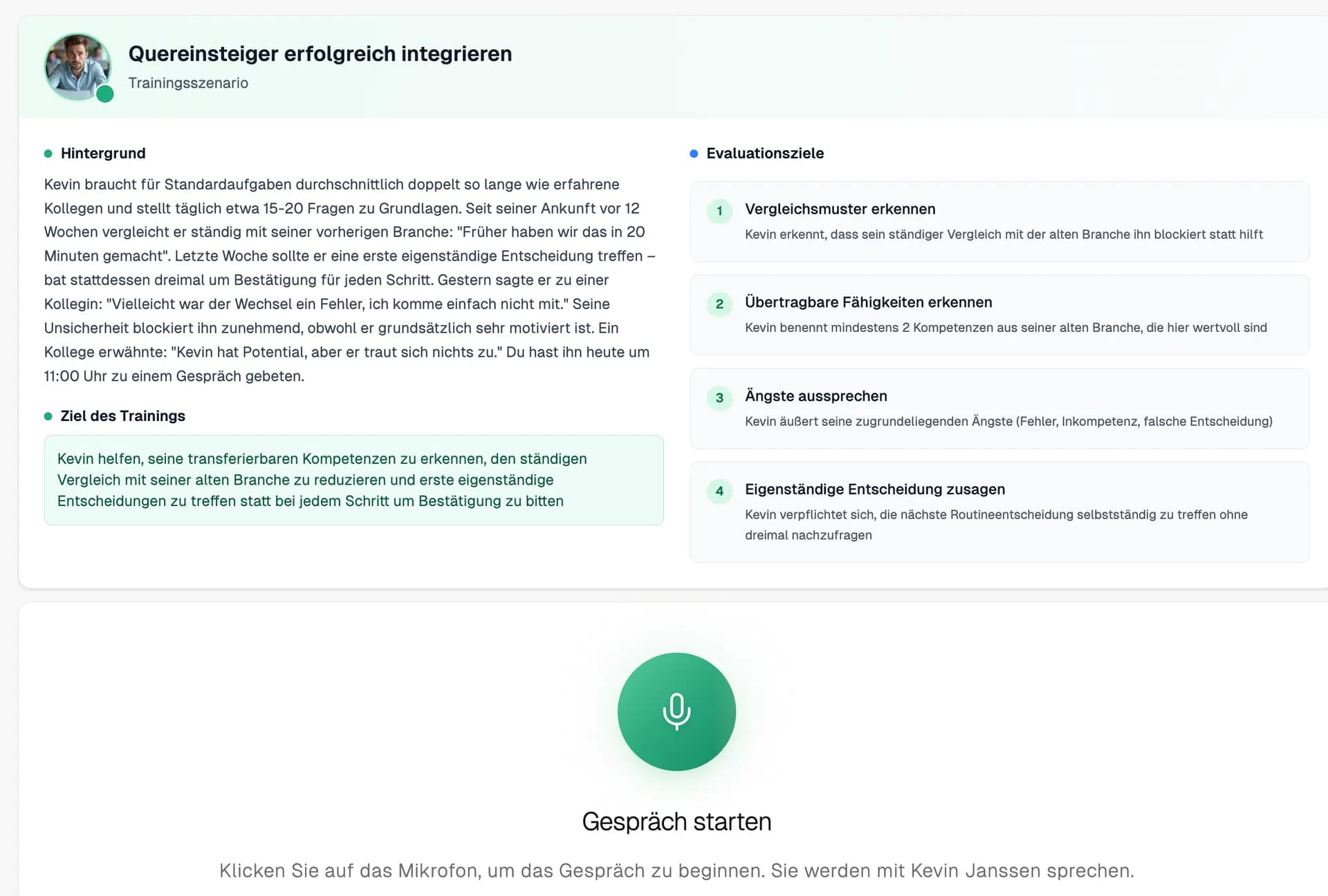
When AI role-plays are (still) not the right solution
- Pure knowledge transfer For theoretical foundations (labor law, compliance rules, company policies), e-learning modules are more efficient. AI role-plays start where knowledge needs to be translated into practical conversational competence.
- One-time interventions without follow-up If continuous use is not planned after an initial training, the implementation effort is not justified. The strength lies in repeated practice over months.
- Teams with fewer than 5 leaders For very small teams, individual coaching can be more cost-effective. The scaling advantages of AI systems only kick in with approximately 8-10 leaders.
- Lack of technical infrastructure A stable internet connection and basic IT literacy are prerequisites. In production environments without computer workstations, alternative solutions must be found.
How to successfully roll out AI role-plays?
Phase 1: Strategic Preparation (2-4 weeks)
Conduct a needs analysis
Start with a systematic inventory of your leadership challenges:
- Which types of conversations cause the most difficulties?
- Where do most avoidable problems arise?
- What differences exist between departments?
Practical Tip: Conduct 30-minute interviews with 5-8 leaders from different areas. Don't ask about training needs, but about specific situations: "Tell me about an employee conversation that was difficult – what exactly was the challenge?"
Establish stakeholder management
Involve early on:
- Management: Business case with clear objectives
- Works Council: Transparent communication about data protection and use of learning data
- IT Department: Clarification of technical requirements, SSO integration
- Leadership Representatives: "Champions" from different areas for the pilot phase
Define success criteria
Set measurable goals to be evaluated after 3-6 months:
- Usage rate: At least 70% of leaders complete 3+ scenarios per quarter
- Completion Rate: At least 75% of started conversations are completed
- Quality Goal: Average score continuously increases
- Qualitative Goal: Managers report concrete behavioral changes
Phase 2: Pilot Program (6-8 weeks)
Assemble the pilot group
Strategically select 8-12 managers:
- Mix of Seniority: 40% experienced managers, 60% younger team leaders
- Various Departments: Sales, Production, IT, Administration
- Different Affinity: 30% Early Adopters (tech-savvy), 70% typical users
- Geographical Distribution: From all regions if there are multiple locations
Why this mix? Early adopters provide positive feedback and become multipliers. Skeptics identify real problems that need to be solved before the rollout.
Kick-off and Onboarding (Week 1)
Organize a 90-minute workshop:
- 30 Minutes: Why we are doing this (problem statement, goals, benefits)
- 30 Minutes: Live demo with a real scenario
- 20 Minutes: Technical introduction, account setup
- 10 Minutes: Q&A and expectation management
Critical Success Factor: Have participants conduct their first conversation during the workshop – still in the room, with support. The inhibition threshold drops dramatically when the first experience is positive.
Structured Training Program (Week 2-6)
Instead of free use: clear structure with weekly tasks:
Week 1-2: Basics
- 2 scenarios from the "Feedback Conversations" category
- Focus: Positive reinforcement and constructive criticism
- Goal: Understand the system, reduce inhibition threshold
Week 3-4: Challenges
- 2 scenarios from the "Conflict Conversations" or "Criticism Conversations" category
- Focus: Managing emotional situations
- Goal: Experience realistic difficulty
Week 5-6: Individualization
- Free choice from all available scenarios
- Focus: Personal development areas
- Goal: Establish independent use
Accompanying Measures:
- Weekly reminder emails (short, motivating)
- Bi-Weekly check-ins in small groups (3-4 people)
- Slack/Teams channel for questions and exchange of experiences
Collect and evaluate feedback (Week 7-8)
Quantitative Data (automatically from the system):
- Usage frequency per person
- Completion Rate per scenario
- Average scores and development
- Most frequent drop-off points
Qualitative Insights (through interviews):
- Did the training influence your behavior in real conversations?
- Which scenarios were particularly valuable?
- Where were there technical problems?
- What would facilitate everyday use?
Phase 3: Optimization and Adaptation (3-4 weeks)
Resolve technical issues
Typical pilot insights:
- Audio quality with standard headsets
- Browser compatibility with corporate IT settings
- Mobile use for on-the-go
Refine scenarios
Based on pilot feedback:
- Too generic? Add industry-specific details
- Too easy/difficult? Adjust difficulty levels
- Missing topics? Develop custom scenarios for company-specific challenges
Example: A manufacturing company developed a custom scenario "Employee doesn't take protective equipment seriously" – with production-specific details and terminology. Careertrainer.ai enables such adaptations based on templates within a few days.
Phase 4: Company-wide Rollout (3-6 months)
Change Management: The critical phase
The biggest challenge is not technology, but adoption.
Common resistances and how to address them:
"I don't have time for this." → 15 minutes between meetings are enough for one scenario. That's less time than a postponed critical conversation would cost later.
"AI cannot replace real people." → Correct! It's about a safe practice environment – like a flight simulator for pilots.
"I've been leading for 20 years – I don't need training." → Leadership is changing (Gen Z, Remote Work, Diversity). Even top athletes continuously train fundamentals.
"This feels artificial." → After 2-3 minutes, most people forget they are talking to AI. The characters in Careertrainer.ai are based on the Myers-Briggs model and react so realistically that emotional responses arise – just like in real conversations.
Rollout Strategy: Wave Model
Wave 1 (Month 1-2): Management Level
- Executive Board, Division Heads, Department Heads
- Top-down Signaling: "I am also continuing to develop"
Wave 2 (Month 3-4): Team Leaders and Project Managers
- The largest group, highest impact on employee satisfaction
Wave 3 (Months 5-6): Junior Leaders
- High potentials, future team leaders
- Early development prevents later bad habits
Integration into existing HR processes
AI role-plays unleash maximum impact when integrated into core processes:
Onboarding new leaders:
- Week 1-2: 5 basic scenarios as mandatory training
- Focus: Company culture, communication standards
- Result: New leaders speak "our language" from day 1
Performance Review Cycle:
- Q1: 360° feedback identifies areas for development
- Q2-Q3: Targeted training with specific scenarios
- Q4: Follow-up assessment
Talent Development Programs:
- High potentials train leadership situations before taking on their first personnel responsibility
Crisis Intervention:
- Acute team conflicts? → Training similar scenarios before the real conversation
- Upcoming termination? → Preparation through termination conversation scenario
Phase 5: Continuous Optimization (ongoing)
Data-driven further development
Analytics data shows clear patterns after 3-6 months:
- Which scenarios are trained most frequently? → Shows real pain points
- Where do leaders most often abort? → Scenario too difficult? Too long?
- Which scores remain consistently low? → Identifies skill gaps
- Who isn't using the system? → Personal outreach: "What's holding you back?"
Practical example:
A company found that critical feedback conversations had a completion rate of only 55%, while general feedback conversations were at 82%. Analysis showed: The critical feedback scenario escalated too quickly. Solution: Development of a "Critical Feedback Light" scenario with a gentler reaction. Completion rate rose to 74%.
Building a community
Quarterly "Leadership Labs":
- 90-minute session, 8-12 leaders
- Everyone brings their most difficult scenario
- Group discusses alternative approaches
Internal Champions Program:
- 5-8 power users become mentors
- Offer "Office Hours" for colleagues
Systematically collect success stories:
- Monthly survey: "Did training help last week?"
- Share best cases in the newsletter (anonymized)
What can be measured specifically?
Measurability is a crucial advantage of AI role-play platforms. Here's what systems like Careertrainer.ai capture:
Team-Level Analytics: The Overview for HR
Usage Metrics:
- Active users (7/30 days)
- Total sessions and per period
- Completion Rate (Goal: >75%)
- Average Session Length
Performance Metrics:
- Average Score across all scenarios (Scale 1-10)
- Score Development over Time (8-week trend)
- Scenario vs. Baseline Performance: Do leaders achieve specific learning objectives (70%) better than generic communication skills (30%)?
Scenario-specific Insights:
Most Played Scenarios: Shows the biggest pain points. If "Critical Feedback Conversations" is #1 → HR knows: This is the current challenge.
Lowest Completion Rates per Scenario: Which conversations are particularly challenging? Indicator for difficulty or need for adaptation.
Average Scores per Scenario: Where are teams strong, where are they weak?
- Feedback Conversations: Avg. 7.8 → Team is good at praising
- Conflict Conversations: Avg. 5.9 → Clear need for development
→ HR Action: Workshop on "Conducting Difficult Conversations"
Category Analysis: Which topic areas dominate? Careertrainer.ai shows, for example:
- 35% Performance Reviews
- 28% Feedback Conversations
- 22% Conflict Management
- 15% Development Conversations
Individual-Level Insights: Personalized Development
Personal Performance Overview: Each leader sees:
- Completed scenarios with scores
- Strengths and weaknesses across all conversations
- Improvement over time (trend curve)
- Optional: Comparison with team average
Detailed Feedback after each conversation:
Scenario Performance (70% weighting): Were the specific learning objectives achieved?
Example "Fostering an insecure employee":
- ✅ Employee named 2 of her own strengths (30 points)
- ✅ You mentioned 3 concrete examples of success (25 points)
- ⚠️ No personal strategy developed (0 out of 25 points)
- ❌ Anti-Pattern: Built pressure instead of encouraging (-15 points)
Baseline Skills (30% weighting): Generic leadership competencies:
- Active Listening: 8/10 (good questioning and paraphrasing)
- Empathy: 6/10 (room for improvement, overlooked emotional signals)
- Conversation Management: 7/10 (good structure, but too directive)
Concrete Suggestions for Improvement: "The employee showed signs of being overwhelmed (longer pauses, broken sentences). You could have slowed down the pace with: 'Let's pause for a moment – what's on your mind right now?'"
Skill-Gap Identification:
The system recognizes recurring patterns:
A leader completes 5 scenarios. Analysis shows:
- Strength: Active Listening consistently at 8-9/10
- Weakness: Empathy consistently at 5-6/10
- Anti-Pattern: Rushed to a solution too quickly in 4 out of 5 conversations
→ System Recommendation: "Your conversation style is structured, but you often jump into solution mode too quickly. Try this: Ask 3 open-ended questions before offering a solution."
Training Recommendations:
- "You're strong in feedback discussions – ready for the next challenge? Try 'Moderating a conflict discussion between two team members.'"
- "Critical feedback discussions are still challenging – practice the 'light' version first."
Qualitative Success Metrics
Beyond analytics, qualitative indicators are important:
Behavioral change in daily work:
- Managers report concrete situations where training has helped
- Employee feedback shows improvements in communication
Cultural change:
- Difficult conversations are no longer postponed
- A more open feedback culture emerges
- More consistent leadership standards are established
Engagement and motivation:
- Managers continue to use the system voluntarily
- Peer learning and exchange emerge organically
Adaptation to Corporate Culture and Industry
Why Standard Solutions Are Not Enough
A mechanical engineering company has different leadership challenges than an IT service provider. Careertrainer.ai enables comprehensive customization:
Integration of company-wide leadership guidelines:
- Upload your leadership principles and communication standards
- AI is trained with company-specific guidelines
- Compliance requirements and diversity principles are incorporated into the training
Industry-specific scenarios:
Example Mechanical Engineering:
- Safety discussions in production
- Empathically communicating quality problems
- Professional shift handovers
Example IT Service Provider:
- Burnout prevention for developers
- Communicating customer projects internally
- Explaining agile methods clearly
Developing Custom Scenarios: HR developers can create fully individualized training scenarios based on templates – characters, situations, evaluation criteria, and learning objectives are adapted to specific company challenges.
Technical and Legal Aspects
GDPR Compliance
German companies must exercise particular diligence with AI systems:
- Server location Germany
- Encrypted data storage
- No use of training data by external LLMs
- Transparent documentation of data processing
Careertrainer.ai meets these requirements: servers in Germany, GDPR-compliant data processing, no sharing with AI training.
Works Council and Co-determination
When introducing new learning systems, works councils have co-determination rights:
- Early involvement
- Transparent communication about functionality
- Clear regulations for the use of learning data
Compliance Documentation
AI training systems must consider industry-specific compliance requirements and offer appropriate documentation capabilities.
Future Outlook
Predictive Analytics
Future systems will identify leadership problems before they arise. By analyzing communication patterns and training behavior, development needs can be identified early.
Advanced Personality Simulation
The further development of emotional AI enables even more realistic character simulations. Careertrainer.ai already uses the Myers-Briggs model with 16+ different personality types – in the future, subtle emotional nuances and complex personality structures will be trainable with even greater precision.
Conclusion
Leadership skills are not developed in theoretical seminars, but through practical exercise in realistic situations. AI-supported role-playing games systematically bring this practice into training for the first time – individually adaptable, scalable, and measurable.
The core advantages for HR teams:
Scalability: From 1 to 1000 managers without additional trainer capacities Measurability: Team analytics show learning progress, skill gaps, and training effectiveness Individualization: Adaptable to corporate culture, industry, and specific challenges Sustainability: Continuous training instead of one-off events Security: Risk-free practice environment for emotionally challenging conversations
Next Steps:
- Needs analysis: Interviews with managers about specific challenges
- Stakeholder management: Involve management, works council, IT early
- Pilot program: 8-12 managers, 6-8 weeks of structured training
- Optimization: Technical and content adjustments based on feedback
- Rollout: Wave model over 3-6 months with professional change management
The technology is available, and initial companies are gaining valuable experience. The crucial question is no longer whether innovative training methods will come, but when HR teams will take the step to elevate leadership development to the next level.
